The Accelerating Pace of GenAI: A Moore’s Law Trajectory and its Impact on Analytic Services
The Accelerating Pace of GenAI: A Moore’s Law Trajectory and its Impact on Analytic Services
Introduction
Generative AI (GenAI) has entered a phase of rapid advancement, echoing the exponential growth once attributed to Moore’s Law in transistor density. Much like the transformative effect of increasing computing power on software and hardware innovation, GenAI’s expanding capabilities are poised to revolutionize how organizations approach data analysis, automation, and strategic decision-making. This text expands on the foundational article to illustrate GenAI’s accelerating development, analyze the primary drivers behind its growth, and explore its impact on analytic services—especially GenIP’s Invention Evaluator. Lastly, it highlights how these advancements stand to benefit GenIP shareholders.
The “AI Moore’s Law” Concept
Moore’s Law famously predicted that transistor counts on integrated circuits would roughly double every two years, driving down computing costs and fueling technological progress. Researchers now observe a similar exponential trend in GenAI’s capabilities:
- Consistency in Task Completion
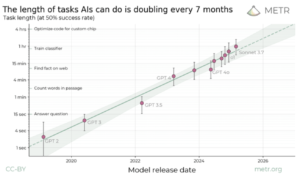
A study from Metr.org indicates that the maximum length and complexity of tasks AI systems can handle effectively is doubling approximately every seven months, rather than every two years . This performance leap underscores how swiftly model architectures, training methods, and computational resources are evolving. - Scaling Laws
Work by Kaplan et al. (2020) shows that language model performance scales predictably with increases in model size, computational power, and data availability . This implies clear pathways for future breakthroughs—simply put, more data plus more processing power yields better-performing models. - Efficient Algorithms and Hardware
Innovations in transformer architectures (e.g., “Attention is All You Need” by Vaswani et al.) have made it easier to train large-scale models with parallelized computation . Simultaneously, the proliferation of specialized AI hardware (GPUs, TPUs, and other accelerators) reduces training time and cost, driving adoption and continuous improvement. - Data Availability and Infrastructure
A global surge in digitized information means GenAI can learn from ever-larger and more diverse datasets. Cloud computing platforms further reduce infrastructure barriers, allowing organizations of all sizes to harness powerful models without large on-premise server investments.
Key Drivers of Accelerating GenAI Capabilities
Although the “AI Moore’s Law” analogy is broad, it is underpinned by several concrete drivers:
- Novel Algorithmic Innovations
Research in attention-based transformer architectures and reinforcement learning has consistently yielded better performance for language tasks, code generation, reasoning, and more. As these algorithms become standardized, the speed of model development has quickened. - Open-Source Collaboration
Many cutting-edge tools and research findings are shared openly, lowering the barrier to entry for organizations and academics who want to experiment with or refine GenAI models. - Growing Commercial Interest
Companies see GenAI as a strategic differentiator, leading to extensive funding and resource allocation. This virtuous cycle—investment → research → results → more investment—further accelerates GenAI’s trajectory.
Impact on Analytic Services
As GenAI capabilities expand, analytic services are experiencing a paradigm shift:
- Automated Data Analysis
Large language models can automate labor-intensive processes, from data cleaning to sophisticated statistical analysis, enabling data teams to devote more time to high-level strategy and interpretation. - Natural Language Querying
With user-friendly interfaces—often built on top of GenAI—business users can pose queries in plain language, reducing reliance on specialized data teams. - Predictive Modeling and Forecasting
Improved model architectures yield more accurate predictions for sales, logistics, finance, and other critical functions. Over time, better forecasts can translate into competitive advantage and cost savings. - Anomaly Detection
Advanced AI systems can detect subtle patterns in large datasets—whether for cybersecurity, fraud detection, or quality control—that might remain invisible to human analysts. - Automated Content Generation
From generating detailed reports to creating succinct executive summaries and visualizations, GenAI can handle routine communication, freeing analysts to focus on insights and recommendations.
GenIP’s Invention Evaluator: Poised to Harness GenAI’s Growth
GenIP’s Invention Evaluator is a key example of how these GenAI-driven innovations translate into tangible results. The service leverages GenAI models to assess an invention’s novelty, commercial potential, and alignment with existing patent landscapes. As GenAI matures, the Invention Evaluator benefits in several ways:
- Enhanced Patent Analysis
Large language models, trained on massive corpora of patent filings, learn to spot nuanced similarities and differences in technical descriptions more effectively and consistently than earlier AI approaches. - Refined Natural Language Processing
Advances in NLP enable robust keyword extraction, semantic similarity checks, and contextual understanding of patent documents, making it simpler to gauge overlaps or potential conflicts in prior art. - Faster, Automated Prior Art Searches
By automatically crawling patent databases, technical literature, and even relevant open-source projects, GenIP’s Invention Evaluator reduces both the cost and duration of the screening process. - Predictive Patent Valuation
Drawing on scaling laws for AI, the Invention Evaluator can incorporate sophisticated predictive models to estimate patent value and market potential, providing crucial insights for investment decisions.
Benefits to GenIP Shareholders
As GenAI continues its rapid evolution, GenIP shareholders stand to gain significantly from improvements in the Invention Evaluator and related analytic offerings:
- Stronger ROI
More accurate and efficient assessments mean fewer missed opportunities for high-value patents and better resource allocation to the most promising projects. - Reduced Operational Costs
With GenAI taking on routine tasks such as prior art searches, GenIP can devote more of its workforce to strategic research and client-facing innovation, decreasing overhead without sacrificing quality. - Increased Market Competitiveness
Higher evaluation precision and speed can position GenIP as a leader in patent analytics, boosting the company’s reputation and pricing power. This favorable market perception can, in turn, support share price growth. - Long-Term Strategic Partnerships
Trust in the reliability of GenIP’s technology fosters deeper relationships with inventors, research institutions, and corporate partners. These relationships can strengthen the company’s value proposition and generate recurring revenue streams. - Enhanced Innovation Pipeline
By leveraging predictive models to gauge the viability of new inventions, GenIP can channel resources toward the most compelling intellectual property assets, fostering a self-sustaining cycle of innovation and improved profitability.
Conclusion
GenAI’s breakneck progress—marked by gains in computational power, algorithmic innovation, and data availability—mirrors the spirit of Moore’s Law. This exponential growth has profound implications for analytic services, enabling powerful automation, higher accessibility, and richer predictive capabilities. GenIP’s Invention Evaluator exemplifies how these breakthroughs elevate traditional workflows, speeding up patent analysis and improving the precision of novelty and market assessments. For GenIP shareholders, these technological strides translate into tangible upsides: enhanced report quality, improved ROI, cost savings, and a stronger market position that should continue to compound as GenAI matures.
by Melissa Cruz, CEO of GenIP.
References
- “Measuring AI’s Ability to Complete Long Tasks,” Metr.org, March 19, 2025.
https://metr.org/blog/2025-03-19-measuring-ai-ability-to-complete-long-tasks/ - Kaplan, J., McCandlish, S., Henighan, T., et al. (2020). “Scaling Laws for Neural Language Models.”
https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.08361 - Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., et al. (2017). “Attention is All You Need.”
https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762 - https://arxiv.org/abs/2503.14499

